The Gateway Project, located at the University of California, Berkeley, embodies a bold step toward sustainable construction.
Designed by Weiss / Manfredi and executed by Gensler, this impressive structure spans 400,000 square feet and features a unique custom curtainwall façade. This innovative design not only enhances the building’s aesthetic appeal but primarily focuses on reducing its carbon footprint.
The Gateway Project’s curtainwall façade successfully minimizes environmental impact by 15%, showcasing how thoughtful architectural design can contribute to sustainability. As the construction industry significantly contributes to global carbon emissions, finding ways to incorporate eco-friendly materials and practices has never been more critical.
The project’s advancements highlight the urgent need to address climate change within the built environment.
By choosing to implement sustainable solutions in its design, the Gateway Project sets a benchmark for future buildings. As urban areas continue to expand, this project demonstrates a practical approach to meeting the challenges faced by the construction industry while promoting energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Sustainability and Construction

Sustainability plays a crucial role in the construction industry by addressing environmental concerns and promoting responsible practices.
This section explores how sustainable construction reduces emissions and highlights innovative materials that support these goals.
The Role of Sustainable Construction
Sustainable construction focuses on minimizing the negative impact that building activities have on the environment. This approach emphasizes using resources efficiently and responsibly.
It also promotes energy-efficient designs, which reduce energy consumption during the building’s lifecycle.
Moreover, sustainable construction seeks to lower waste through recycling and reusing materials. These practices help conserve natural resources and reduce landfill burden.
By prioritizing sustainability, the industry can contribute to a healthier planet and create structures that stand the test of time.
Reducing Emissions in Construction
The construction sector is responsible for a significant portion of global emissions. It accounts for about 38% of total emissions, largely due to energy use and materials production.
Reducing these emissions is vital for combating climate change.
To make progress, many companies are adopting greener practices. This includes using renewable energy sources and more efficient machinery.
Implementing strategies like optimizing transportation routes also cuts down on fuel consumption.
Furthermore, the use of low-carbon materials, such as recycled steel and eco-friendly concrete, significantly lessens emissions. By innovating construction processes, the industry can significantly reduce its carbon footprint.
Innovations in Sustainable Materials
Innovative materials are central to achieving sustainability in construction. These materials often come from renewable resources or have a lower environmental impact than traditional options.
For instance, bamboo is gaining popularity due to its strength and rapid growth rate.
Other advancements include high-performance insulation and energy-efficient windows, which help buildings remain comfortable while using less energy. The development of self-healing concrete can also extend a structure’s life, which reduces the need for repairs and new materials.
Additionally, technology such as 3D printing allows for more precise material usage, reducing waste. By embracing these innovative materials, the construction industry can make significant strides toward a sustainable future.
The Carbon Footprint of Building Materials

The carbon footprint of building materials plays a crucial role in construction sustainability. Understanding embodied carbon, lifecycle impacts, and Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) helps identify ways to reduce emissions and promote more eco-friendly practices.
Embodied Carbon in Materials
Embodied carbon refers to the total greenhouse gas emissions that occur during the production and transportation of building materials. This includes everything from raw material extraction to manufacturing and delivery.
Certain materials, like cement and steel, have high embodied carbon compared to others, like wood or recycled materials.
For example, the production of cement alone is responsible for about 8% of global CO2 emissions.
Reducing the use of high-embodied carbon materials is vital in decreasing overall carbon footprints in construction projects. This can involve the use of alternative materials or more efficient building techniques.
Lifecycle Environmental Impacts
Lifecycle environmental impacts consider emissions at all stages of a building’s existence. This includes production, construction, operation, maintenance, and eventual demolition. Each stage contributes differently to the total carbon footprint.
Book Your Dream Vacation Today
Flights | Hotels | Vacation Rentals | Rental Cars | Experiences
During the operational phase, energy consumption for heating and cooling significantly adds to emissions. Materials that promote energy efficiency help lower emissions during this stage.
Additionally, waste generated during demolition also impacts carbon output. Using recyclable materials can help minimize this effect and promote a more sustainable lifecycle for buildings.
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs)
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) are standardized documents that provide detailed information about a product’s environmental performance. These declarations include data on embodied carbon, energy usage, and other impacts throughout a product’s lifecycle.
EPDs enable architects and builders to compare materials based on their environmental effects. This transparency supports informed decisions aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of construction projects.
By choosing products with lower carbon emissions according to EPDs, the construction industry can progressively shift towards environmentally friendly practices.
Curtain Wall Systems and Architecture

Curtain wall systems play a crucial role in modern architecture, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency. By incorporating advanced materials and design techniques, architects can create structures that are not only visually striking but also environmentally responsible.
Designing for Efficiency
In architectural design, efficiency is a key factor. Curtain wall systems allow for large expanses of glass, which can flood interiors with natural light. This reduces the need for artificial lighting, leading to lower energy consumption.
Additionally, many curtain walls are designed with thermal performance in mind. Features like insulated glazing and weather-tight seals help maintain consistent indoor temperatures. This energy efficiency is vital in reducing the overall carbon footprint of buildings.
The Role of Curtain Walls in Sustainability
Curtain walls significantly contribute to sustainable building practices. By improving energy efficiency, they help decrease carbon emissions associated with heating, cooling, and artificial lighting. According to experts, buildings with advanced curtain wall systems can achieve higher performance ratings.
These systems also enable the use of recycled and sustainable materials. Integrating such materials into construction aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. Sustainable curtain walls represent a shift towards a more environmentally friendly building sector.
Custom Curtainwall Case Study: Gateway Project
The Gateway Project showcases the advantages of a custom curtainwall façade. Designed by Weiss / Manfredi and Gensler, this project spans 400,000 square feet. The custom design focuses on reducing the carbon footprint while enhancing the building’s aesthetics.
This façade incorporates innovative materials and techniques that minimize environmental impact. With documented proof of its reduced carbon emissions compared to industry averages, the project sets a benchmark for future architectural designs. The Gateway Project exemplifies how custom curtain walls can lead to substantial sustainability achievements in construction.
Standards and Certifications in Construction

Standards and certifications play a crucial role in guiding sustainable practices in the construction industry. They help ensure buildings are designed and built to minimize environmental impact while promoting occupant health and well-being. Key frameworks in this area include LEED, WELL, and the Living Building Challenge.
LEED and Building Efficiency
LEED, or Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, is a widely recognized certification that promotes sustainable building practices. It focuses on various aspects, including energy efficiency, water use, and indoor air quality.
LEED offers several ratings: Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, based on points earned in different categories.
Projects aiming for LEED certification might integrate energy-efficient systems, like solar panels, and use sustainable building materials to reduce their carbon footprint.
These practices not only align with goals for net-zero emissions but also enhance occupant comfort and productivity. LEED-certified buildings can benefit from lower operating costs, making them appealing to investors and owners alike.
Emerging Construction Standards
New standards are continually emerging to address sustainability and health in building design.
The WELL Building Standard focuses on promoting health and wellness in indoor environments. It evaluates features like air quality, natural light access, and fitness options.
Another significant standard is the Living Building Challenge, which requires buildings to meet net-zero energy, water, and waste goals. It pushes designers and builders to rethink traditional strategies and opt for innovative, sustainable solutions.
The Passive House standard emphasizes energy efficiency through superior insulation and airtight construction. Meanwhile, Fitwel is a newer standard that highlights design strategies promoting occupant health.
These evolving frameworks reflect a growing recognition of the construction industry’s role in sustainability and public health initiatives.
Collaborations for a Sustainable Future

The Gateway Project demonstrates how strategic partnerships can advance sustainability in construction. Through effective collaboration among industry leaders and academic institutions, innovative solutions for reducing carbon footprints have emerged.
Strategic Industry Partnerships
Turner Construction plays a critical role in the Gateway Project by partnering with other key players in the construction industry. These partnerships streamline the supply chain, ensuring that sustainable materials and methods are prioritized. The use of a custom curtainwall façade is one significant outcome of this collaboration.
This design not only minimizes environmental impact but also meets durability and aesthetic goals. Industry collaboration leads to knowledge sharing, which fosters innovation. For instance, adopting low-carbon concrete and other sustainable materials enhances construction efficiency while lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Academic Contributions to Sustainability
Collaboration with institutions like UC Berkeley adds substantial value to the project. The university’s College of Computing contributes cutting-edge research and innovative ideas that bolster sustainable practices.
Students and faculty are directly involved, lending expertise in areas such as energy efficiency and sustainable design principles. Their findings help inform the project’s strategies, enabling real-world applications of academic research. This partnership exemplifies the fusion of theory and practice, laying a foundation for a future where sustainable architecture is the norm rather than the exception.
Toward Net Zero Carbon Construction
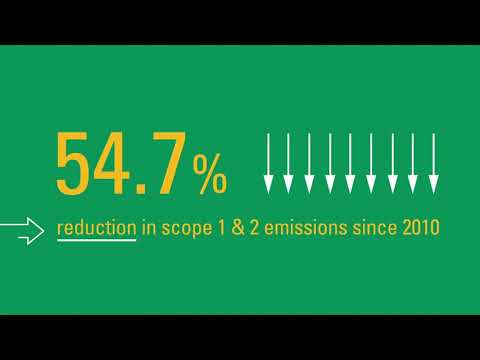
Achieving net zero carbon in construction requires understanding the challenges and identifying effective solutions. Monitoring progress and reporting on carbon footprints are essential for building accountability and transparency.
Challenges and Solutions
The path to net zero carbon construction is filled with obstacles. One major challenge is the high embodied carbon in materials used for building. Many traditional building materials have significant carbon footprints due to their extraction and processing.
To tackle this, the industry is shifting towards using more sustainable materials.
Utilizing products with Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) provides detailed information about their environmental impacts. Additionally, the adoption of an embodied carbon database can help builders select low-carbon options.
Collaboration among stakeholders, including architects and contractors, promotes innovation. This teamwork can lead to better designs that minimize carbon emissions while maintaining structural integrity.
Monitoring and Reporting
Tracking carbon emissions throughout the construction process is essential. It allows for real-time adjustments and improvements. Monitoring tools help keep projects aligned with carbon reduction commitments.
Implementing a standardized reporting framework is critical. Such frameworks ensure consistent communication regarding carbon footprints across projects. This transparency fosters accountability and encourages continuous improvement.
Companies can categorize their projects based on carbon impact, helping them make informed decisions. Regular assessments contribute to refining strategies for achieving net zero emissions, which is vital for the future of sustainable construction.
Global Perspectives and Action

The construction industry plays a significant role in global warming and carbon emissions.
Different regions have adopted various practices and standards to address sustainability in buildings.
This section highlights the role of construction in global warming and examines international practices aimed at reducing environmental impacts.
Role of Construction in Global Warming
The construction industry accounts for a substantial portion of global emissions. It generates approximately 38% of total carbon emissions. This impact is equivalent to the emissions produced by building cities the size of Paris every week.
Each phase of a building’s life—construction, operation, and demolition—contributes to its global warming potential.
For example, in cities like London and Sydney, regulations increasingly focus on improving energy efficiency and minimizing waste.
Adopting sustainable materials and technologies can significantly lower emissions.
Innovations like energy-efficient curtainwall facades, such as the one used in the Gateway Project, showcase the potential for reducing the carbon footprint in construction. This approach not only addresses current emissions but also sets a precedent for future projects.
International Practices and Standards
Many countries are adopting international standards to promote sustainability in construction.
In Shanghai, local initiatives aim to create greener buildings, emphasizing reduced energy consumption and enhanced environmental performance.
International organizations often set guidelines to help the construction industry meet environmental goals. For instance, the LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification encourages ecologically sound practices globally.
Cities like London are adopting stricter building codes that require substantial reductions in carbon emissions. These regulations guide architects and builders in using materials and designs that prioritize sustainability.
By balancing technological advancement and ecological responsibility, these practices contribute to a more sustainable future for the construction industry on a global scale.
Conclusion

The Gateway Project demonstrates a significant step toward a more sustainable future in construction. Its custom curtainwall design effectively reduces the carbon footprint, showcasing the potential of innovative materials.
Key Benefits:
- Lower Embodied Carbon: By using sustainable construction materials, the project meets lower embodied carbon targets.
- Combatting Climate Change: This approach helps in mitigating the impacts of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Constructing buildings with a focus on sustainability is essential.
The construction industry is responsible for a large portion of global emissions. Therefore, adopting greener practices is crucial for the environment.
The use of advanced design and materials, like those in the Gateway Project, can set a new standard in the field.
As more projects embrace similar strategies, a shift towards sustainable practices becomes increasingly attainable.
Such efforts not only benefit the planet but also inspire other builders and architects.
The successful implementation of this project can motivate further advancements in sustainable construction.
By prioritizing eco-friendly designs, the construction industry can move toward a more responsible future.
Book Your Dream Vacation Today
Flights | Hotels | Vacation Rentals | Rental Cars | Experiences